The Problem
CLI-based coding agents (Claude Code, Cursor) couldn’t autonomously validate proprietary language syntax, forcing developers into manual debugging loops that broke the AI-assisted development flow.
When working with XanoScript (Xano’s proprietary backend language), AI agents would generate code with syntax errors they couldn’t detect. Developers had to:
- Copy code to the Xano IDE
- Run manual validation
- Copy errors back to the AI
- Wait for the AI to fix it
- Repeat the cycle
This manual debugging loop destroyed the productivity gains of AI-assisted development.
The Solution
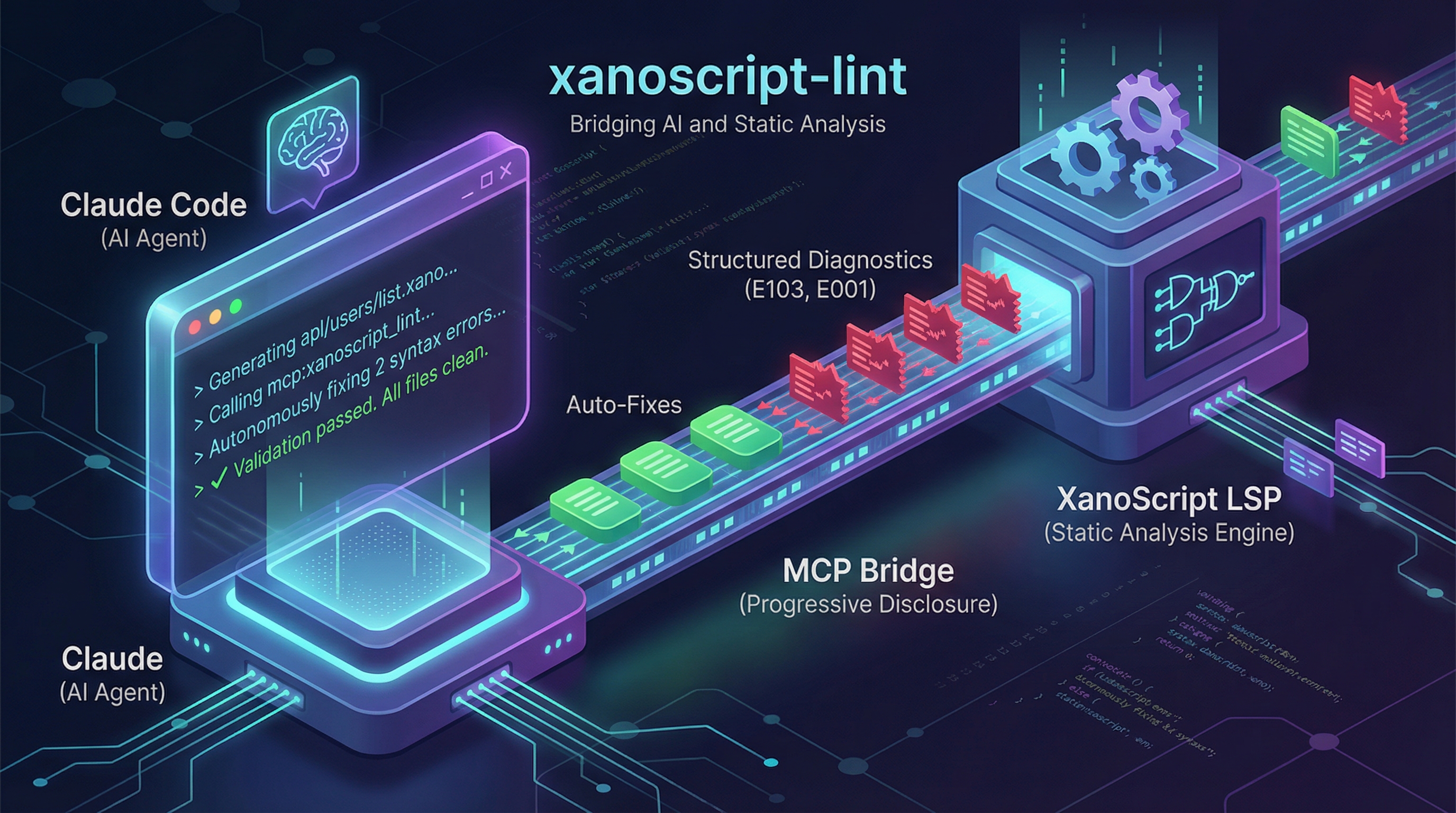
I built a Node.js CLI tool that bridges the Language Server Protocol (LSP) with LLM agents via Claude Skills (MCP integration).
Instead of dumping all diagnostic data into the context window (which would overflow the token limit), the tool implements progressive disclosure:
- The AI requests diagnostic data only when needed
- Error information appears on-demand during the conversation
- Context windows stay clean and optimized
Key Innovation: Progressive Disclosure
Traditional approaches either:
- Dump everything → Overflow context window, confuse the model
- Provide nothing → Agent can’t self-correct
xanoscript-lint uses progressive disclosure via Claude Skills:
- The AI can ask for linting results when it wants to validate
- Diagnostics appear as structured tool responses, not raw dumps
- The agent learns when to check its work vs. when to keep generating
This mimics how human developers work: write code, then validate, then fix—not validate every single line as you type.
Developer Experience Impact
Before xanoscript-lint:
- Developers manually copied code between AI and IDE
- 5-10 minute debugging cycles per error
- Lost flow state with context switching
After xanoscript-lint:
- Agents self-correct 7+ syntax errors across multiple files simultaneously
- Zero manual debugging cycles
- Developers stay in flow with the AI handling validation
Technical Architecture
Components
-
XanoScript Language Server
- Provides syntax validation
- Returns structured diagnostic data
- Follows LSP specification
-
Claude Skill (MCP Integration)
- Exposes
xanoscript_linttool to Claude Code - Agent can invoke: “Check this file for errors”
- Returns formatted error messages with line numbers
- Exposes
-
CLI Wrapper
- Symlinks skill into project
.claudedirectory - Manages Language Server lifecycle
- Handles file-system operations
- Symlinks skill into project
Workflow
Developer writes prompt → Claude Code generates XanoScript
↓
Agent invokes xanoscript_lint skill (MCP tool use)
↓
CLI calls Language Server with file path
↓
LSP returns structured diagnostics
↓
Agent receives formatted errors in context
↓
Agent autonomously fixes errors and re-validatesContext Management Strategy
The breakthrough was treating validation as a tool, not as ambient context.
Bad approach: Include all possible errors in system prompt
- Wastes tokens on files with no errors
- Confuses agent with irrelevant information
- Breaks down with multiple files
xanoscript-lint approach: Let agent request validation
- Only uses tokens when agent asks
- Agent learns to validate after generating code
- Scales to multi-file projects
This is progressive disclosure in action: information appears when needed, not before.
Multi-File Error Correction
The agent can orchestrate complex fixes:
- Generate code across 3-4 files
- Validate each file using
xanoscript_lint - Identify cross-file dependency errors
- Fix all errors in dependency order
- Re-validate until clean
Example: Agent fixed 7 syntax errors across 4 API endpoint files in a single conversation, including:
- Missing function parameters
- Incorrect variable references
- Malformed SQL queries
- Authentication logic errors
All without human intervention.
Technical Implementation
Language: Node.js + TypeScript Integration: Claude Skills (MCP-style tool use) Protocol: Language Server Protocol (LSP) Deployment: npm package with CLI
Core Innovation:
- Feedback loop between generative AI (Claude) and deterministic static analysis (LSP)
- Agent acts autonomously but validates rigorously
- Combines “creative” and “precise” AI capabilities
DX Optimization
xanoscript-lint solves the “text-to-code” workflow friction:
Old workflow:
- Describe feature to AI → 2 minutes
- AI generates code → 30 seconds
- Copy to IDE, validate, copy errors back → 5 minutes
- AI fixes errors → 30 seconds
- Repeat steps 3-4 until clean → 10-20 minutes total
New workflow:
- Describe feature to AI → 2 minutes
- AI generates + self-validates + self-corrects → 2 minutes
- Done → 4 minutes total
5x faster iteration by eliminating manual debugging loops.
Engineering Depth
This project demonstrates:
- AI-assisted development workflows: Understanding how agents think and when they need validation
- DX optimization: Removing friction from developer workflows
- Tool-use orchestration patterns: Designing tools that agents can invoke autonomously
- Context management: Progressive disclosure to avoid token waste
- LSP expertise: Integrating with Language Server Protocol
- MCP/Skills architecture: Building tools that work across AI platforms
What I Learned
The best AI tools don’t just generate—they validate.
Most AI coding tools are “fire and forget”: generate code, hope it works. xanoscript-lint closes the loop: generate → validate → fix → validate again.
This pattern applies beyond linting:
- AI generates SQL → validate schema
- AI generates API calls → validate endpoints exist
- AI writes tests → validate they compile
Progressive disclosure is the key to scaling AI context windows.
Instead of dumping everything into context, design tools the AI can invoke when needed. This:
- Reduces token usage
- Improves agent decision-making
- Scales to complex multi-file projects
Key Outcomes
- Autonomous error correction: Agents self-correct 7+ errors across multiple files without human intervention
- Developer productivity: 5x faster iteration by eliminating manual debugging loops
- Context optimization: Progressive disclosure keeps token usage low while maintaining validation accuracy
- Proof of concept: Demonstrated that LSP + MCP integration enables sophisticated AI-assisted development workflows
Open Source
xanoscript-lint is available as an open-source npm package, demonstrating MCP/Skills integration patterns that other developer tool builders can learn from.
Links
- GitHub Repository (coming soon)
- npm Package (coming soon)
- Technical Deep Dive - Dev.to (coming soon)